Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (42): 7462-7468.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.42.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical application of bioabsorbable polymer interbody fusion cage
Wang Le, Liu Shao-yu
- Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2013-03-15Revised:2013-03-29Online:2013-10-15Published:2013-10-31 -
Contact:Liu Shao-yu, Professor, Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China gzsyliu@tom.com -
About author:Wang Le☆, Studying for doctorate, Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China wanglehk@163.com -
Supported by:the Major Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China in 2010, No. C1032001*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Le, Liu Shao-yu. Clinical application of bioabsorbable polymer interbody fusion cage[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(42): 7462-7468.
share this article
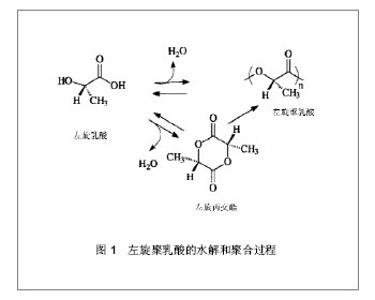
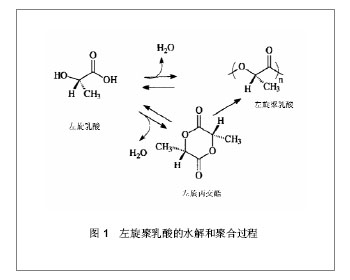
2.1 融合器材料 2.1.1 材料种类 目前矫形外科中应用最多的生物可降解材料是α-多聚酸,由α-羟基酸聚合而成,如以乳酸为单体的聚乳酸和以乙醇酸为单体的聚乙醇酸。在水环境中这些高分子聚合物可以逐渐降解,最终代谢为水和二氧化碳。乳酸和乙醇酸都自然存在于细胞和器官的生理新陈代谢通路中,但是聚乙醇酸降解速度过快,在体内1个月后失去强度,并不适合用于椎间融合器[8]。 近年来可吸收椎间融合器研究最多的基础材料是聚乳酸。乳酸自然存在左旋异构体和右旋异构体两种同分异构体,其单聚物分别为左旋聚乳酸和右旋聚乳酸,它们具备相同的化学和物理性质,左旋聚乳酸使用更普遍。 高聚物不存在完全晶体形态,举例来说,自然构成的左旋聚乳酸有37%的结晶度,当左旋异构体和右旋异构体等量共聚化时(分子链含有等量的左旋异构体和右旋异构体),就形成了消旋聚乳酸。70∶30的聚左旋消旋乳酸(或70/30 聚左旋消旋乳酸)是指左旋异构体左旋聚乳酸分子比例占到70%,左右消旋的聚合物消旋聚乳酸比例占到30%。因此这种聚合物含有85%的左旋异构体和15%的右旋异构体。骨科文献中还有一些少见的混合物,比如80∶20、85∶15和96∶4等,见图1。"
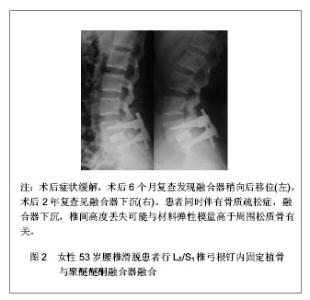
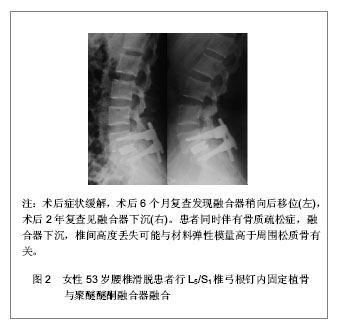
聚己内酯由ε-己内酯开环聚合而成,美国FDA已批准用于人体,因其良好的力学性能、低熔点 (60 ℃)、低玻璃转变温度(-60 ℃)、可低温成型、易于加工、体内缓慢降解等优势而被广泛应用于医疗领域,但仍存在亲水性差、强度不足、降解过程中pH值变化过大等缺陷[9]。 国内还有学者研发出多元氨基酸共聚物/磷酸三钙复合材料,即由多种氨基酸构成的共聚物与磷酸钙原位聚合而制成。所采用的氨基酸依次为6-氨基己酸、甘氨酸、L-丙氨酸、L-脯氨酸、L-苯丙氨酸、L-赖氨酸,其质量比为108∶2∶6∶6∶7∶2,磷酸三钙的质量分数为30%[10-11]。 2.1.2 材料特性 高聚物一个最出色的优点是便于加工出很多理化性质不同的产品,可根据不同的需要量身订制。但是聚合物之间很难相互比较,因为加热过程、内植物设计、体内环境等很多参数都可以影响它们的性能,甚至成分和分子质量相同的聚合物也可能存在不同的特性。评估聚合物最重要的参数是结晶度和平均分子质量,其他为分子质量分布(多分散性),杂质(比如残留单体,水和自由基)含量,玻璃化转变温度Tg。以往认为可吸收融合器的合理Tg应高于体温[12],随着研究深入,混合型材料逐渐增多,原本Tg较低,强度过低的材料如聚己内酯等可与磷酸三钙或羟基磷灰石构成复合材料,满足临床需求。 在所有次要参数一致的情况下,聚合物的结晶度越高其硬度和强度更大,而且降解速度更慢;玻璃转化温度也随着结晶度的增加而升高,这些因素对于脊柱椎间融合器来说十分重要,因其需要承受较高的动态负荷,并且需要在37 ℃环境下能够至少保持作用6个月[13]。 第二个主要影响聚合物特性和降解动力学的因素是分子质量。聚合物分子质量大,结构内缠绕增加促使分子链间二级键的形成,降解需要破坏更多的二级键,所以聚合物强度随着分子质量增加而增大。分子质量有几种不同描述方式,大多数文献使用数量平均分子质量Mn和质量平均分子质量Mw。Mn简单描述聚合物中所有分子链的平均分子质量。而Mw更常用,因为它和聚合物的在融化状态下的黏度有关。Mw测量方法是用分子链线性状态下的质量分数。明显,并不是所有的分子链长度都相同,分子链质量不同,这一特性称为分子质量分布。一个简单的方法来描述分子质量分布就用Mw和Mn的比值;聚乳酸在严格条件下生产,分子质量分布总的来说低于2。分子质量分布大说明Mn较小,即小分子较多,更容易降解。因此,对于生物可吸收聚合物来说,较小的分子质量分布更为重要,它表明分子团的大小差异更小,更容易预测评估其降解率。残余单体含量也与此有关,因为它可算出未聚合的单体分子数量;残余单体含量是聚合物生产的关键,生产者要控制得当。一个常用的确定整体分子质量分布的方法是凝胶渗透色谱分析法(GPC,也被称为体积排除色谱分析法SEC),可以得到整个质量分布的光谱,Mn、Mw、分子质量分布和单体残留量都可测出。Mw也与黏度有关,也可通过黏度计进行实验得出[12]。 玻璃化转变温度Tg是高聚物另外一个重要特性。玻璃态是指非晶体结构的状态,它的力学特性为固体,分子特性为液体。如温度高于玻璃化转变温度Tg,聚合物可以流动时它的弹性模量远低于其玻璃态。这一点对于生物可吸收性椎间融合器很重要,它的Tg应该高于体温。常用聚乳酸类的Tg一般来说是在55-60 ℃,但水可以作为塑化剂将Tg降低,甚至低于体温37 ℃。Tg还取决于机械载荷的时序:玻璃的变形很大程度上取决于单链的运动状态,在长时间的载荷下(比如人体脊柱),这种材料实际上开始发生潜在变化,最终导致内植物较大的变形和骨质微骨折,这种效应在Tg较低的材料中更为明显。 所谓生物相容性好是指可吸收聚合物和它的单体、聚合启动剂、稳定剂、有机溶剂、乳化剂都不应有毒或致癌,其滤过产物、降解产物和代谢产物亦如此。总之,聚乳酸和聚己内酯都被证实具有良好的生物相容性,无毒性[14-15]。 当外来材料植入体内时周围的组织会被挤压或破坏,炎症反应被激活并修复损伤。炎症反应的第一步是调理素作用,即包装血浆蛋白比如免疫球蛋白G(IgG),使融合器成为中性粒细胞的靶点并促进巨噬细胞黏附。中性粒细胞是巨噬细胞和多核巨细胞的先头部队,被激活后的巨噬细胞释放自由基和降解酶类,比如酸性磷酸酶和乳酸脱氢酶,可以影响内植物及其周围组织。局部pH值下降会促使骨溶解等反应的发生:破骨细胞(负责骨吸收的主要细胞)在低pH值环境变得更加活跃,因此可以吸收内植物周围骨质,导致临床上内植物失败。 在早期文献中,0-22%的患者经可吸收聚乳酸或类似聚合物内植物治疗后出现置入处刺激,无菌性窦道或骨溶解。然而排出的引流经常规细菌培养均为阴性,表明生物反应是伴随酸性聚合物降解产物的化学刺激引起的[16]。 聚乳酸、聚乙醇酸和聚己内酯与骨表现出良好的生物相容性,但针对敏感组织比如硬脑膜和神经根的研究有不同结果。聚乙醇酸组成的聚合物置入体内2周后会发生硬膜粘连,因此聚乙醇酸无法作为椎间融合器的材料。而聚己内酯和聚乳酸材料并不发生粘连,也未见组织学上硬膜粘连的不良反应报道。聚己内酯和聚乳酸材料同样也与神经细胞有较好的相容性:脊髓许旺细胞的扩增并未被材料本身或材料的降解产物所影响,而且对神经元细胞、非神经元细胞及轴突的生长均无不良影响。另外,聚乳酸与神经根和外周神经也有较好的生物相容性,这种聚合物制作的管道还被应用于神经修复,因此聚己内酯和聚乳酸相比聚乙醇酸更适合用于椎间融合器的制作[9, 17]。 2.2 可吸收融合器实验研究 目前在椎间融合器的动物研究方面,最主要使用的动物模型是羊。Smit等[ 18]定量分析后认为四足动物尽管不能直立行走,但其脊柱所受应力主要是轴向应力,可以模拟人类脊柱,特别是羊的C3/4节段。 van Dijk等[3]对比了左旋聚乳酸融合器体内模型和体外模型(山羊L3-4节段),发现体内融合器的降解率要高于体外,这可能是由于体内模型中动态应力将水挤入材料孔隙,并挤出代谢产物。他们研究发现相比金属钛合金融合器,左旋聚乳酸组有更高的融合率和更少的并发症,36个月的随访结果显示左旋聚乳酸组中50%的融合器完全吸收,其余的个体仍有1%-10%的融合器残留。他们还指出椎体松质骨的弹性模量平均为2.1-2.4 GPa,但金属融合器的弹性模量为110-200 GPa,与之相比,左旋聚乳酸更接近松质骨,可显著提高椎间融合率。Smit等[19]使用Micro CT重建对脊柱融合区进行了形态学分析,发现骨融合越成熟骨小梁越粗,排列沿轴向越整齐,融合器的弹性模量过高会对这一过程产生不良影响。 Lippman等[20-21]对比了85∶15聚左旋消旋乳酸/聚乙醇酸融合器和70∶30聚左旋消旋乳酸/聚乙醇酸融合器在山羊颈椎前路减压融合手术模型的术后效果,发现前者降解率过快,后者效果与自体骨相当,而添加骨形态发生蛋白2融合率更高。Kandziora 等[22]对比了70∶30聚左旋消旋乳酸融合器和PCC融合器,结果显示PCC组椎间融合率更高,聚左旋消旋乳酸组与自体骨移植效果无显著统计学差异。 Lazennec等[23]认为70∶30聚左旋消旋乳酸融合器与左旋聚乳酸材料相比,降解率更快,更容易诱发炎性反应。他们采用了96∶4聚左旋消旋乳酸融合器在山羊腰椎进行实验,并进行长达3年的随访,影像学和组织学结果显示较高的骨融合率和良好的生物相容性;12个月时可观察到明显的融合器吸收,24个月时完全达到骨性融合,36个月时融合器完全吸收,其效果与自体骨移植相当。 Lyons等[24]应用70∶30聚左旋消旋乳酸材料融合器在绵羊C2/3和C4/5行减压融合手术,术后3个月评估融合情况,发现尽管X射线结果显示所有固定均融合成功,但活检结果显示12只羊中有6只出现了可吸收螺钉或可吸收材料板的断裂,融合率仅为25%。 聚乳酸融合器的机械性能相对较弱。左旋聚乳酸的大块侵蚀,局部高浓度的酸性降解产物最终会导致炎症反应和骨溶解[12, 20],降解速度难以控制,机械强度维持时间有限,内在脆性使其容易在手术操作过程中碎裂[25],因此有必要寻找新的材料。Abbah等[26]报道了一组用猪模型进行的实验,他们设计了一种以聚己内酯为基础混合20%的β-磷酸三钙的椎间融合器用于腰椎前路融合手术,结果未发现材料崩解,假关节形成或对聚己内酯的排异反应;融合器在体内五六个月可维持完好的力学性能,其硬度和强度逐渐降低,2年左右完全代谢。生物力学和组织学结果显示此材料效果相当于自体骨移植,结合骨形态发生蛋白2可优于自体骨。 Ergun等[27]认为Abbah的研究避免了左旋聚乳酸支架的不足,也解决了聚己内酯材料力学性能不足的问题,但该支架是整体蜂窝式布局,不是常规的骨笼结构,并不能植入自体骨加速融合,因此未能满足需求。他们设计了聚己内酯混合羟基磷灰石与磷酸三钙的生物复合材料,通过改变羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙的含量来改变降解率和弹性模量。使用牛脊柱骨体外生物力学实验,对融合情况进行组织学和分子生物学水平的评估,结果表明该材料生物相容性好,且随着羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙的含量增加,骨-融合器接触面所受屈曲应力和骨折阈值均减小。融合器的弹性模量等于或低于植骨面松质骨,可减少接触面脆性骨折的发生和融合失败的风险。 同样,周春光等[11]利用山羊尸体模型测试了多元氨基酸共聚物/磷酸钙复合材料椎间融合器的生物力学,观察12周后认为,虽然术后12周该材料Cage会出现裂缝,但其相对自体髂骨植骨而言表现出更好的负荷分散功能,融合效果更佳。 2.3 可吸收融合器临床应用 目前可吸收椎体间融合器的临床应用有限。文献报道主要有Hydrosorb聚乳酸融合器及70∶30的聚左旋消旋乳酸共聚物(Medtronic Sofamor Danek公司)。2002年椎体间生物可吸收融合器的临床应用效果被首次报道[28]。60例患者行经椎间孔椎体间融合手术后置入椎体网状融合器,未发生融合器相关的并发症,但平均随访时间非常短(4.7个月)。Couture等[29]回顾性研究27例患者行后路腰椎椎间融合手术,双侧置入70∶30聚左旋消旋乳酸的Hydrosorb聚乳酸融合器,术后随访26个月影像学结果显示融合率达到95.5%。2例患者因假关节形成接受翻修手术。他们还发现随着融合节段的增加,患者术后效果满意度下降。 Lanman等[32]报道了一组43例退行性变的患者,行经椎间孔椎体间融合置入Hydrosorb聚乳酸融合器,在骨笼内填入自体骨同时添加骨形态发生蛋白2。共行57个节段的融合,术后6个月CT结果显示融合率达到98%,12个月时发现11例患者椎间出现明显骨桥。所有患者未出现与融合器相关的并发症。 Kuklo等[27]报道了一组患者,18个月内单个或多个节段行经椎间孔椎体间融合手术,术中行柱形椎体融合器置入,融合器以异体骨和骨形态发生蛋白2填充,术后平均随访时间12.4个月,侧位X射线复查结果融合率87%,CT结果融合率97%。报道称未发现与融合器相关的感染或其他并发症。 Coe等[31]进行的一项研究用相同的融合器和相同的手术方法治疗31例患者,不同的是填充Cage时使用的是自体骨,结果融合率基本相同(96.8%),平均随访18.4个月。Vaccaro等[32]率先回顾性分析了8例颈椎前路减压植骨融合手术的患者,术中置入70∶30 聚左旋消旋乳酸融合器,填入骨形态发生蛋白2和自体骨,辅以金属钢板固定,平均随访时间7个月,融合率达到94%。 Debusscher等[20]前瞻性研究了一组行颈椎前路手术患者共20例患者27个椎间隙,融合器采用40%左旋聚乳酸混合60%β-磷酸三钙的生物复合材料,平均随访27个月。结果显示术后效果优良率为85%,颈椎后凸矫正率为95%,融合率96%。融合器完整吸收约需36个月。新型融合器术后长期随访未见矫正丢失或炎症反应。这两种材料的结合取长补短,既维持了椎间隙高度和力学稳定性,也保证了融合器长期缓慢吸收促进骨性融合[32]。 Frost等[33]回顾性分析了9例行后路腰椎椎间融合手术患者,同样置入聚左旋消旋乳酸可吸收融合器,平均随访超过1年,4例患者在CT复查时发现融合器周围出现骨质溶解,其中1例因骨组织发生严重无菌性炎症再次手术取出Cage,1例出现疼痛症状;另2例无临床表现。 上述研究的局限性在于:患者例数相对较少;一个和多个层次的外科医生造成同质性差;没有设立非可吸收融合器的对照组;相对较短的随访时间。另外,没有作者在他们的研究中提到融合器的降解,尽管Coe的研究中平均随访时间超过了这种材料的预期使用寿命。 Jiya等[34]发表了聚左旋消旋乳酸融合器对比传统聚醚醚酮融合器临床疗效的第1篇随机前瞻性研究。他们特别使用了疼痛目测类比(VAS)评分、功能障碍指数ODI及健康调查简表SF-36问卷对患者进行评估,结果显示聚醚醚酮组术后2年除了SF-36一般健康、精神健康和情感分数外,其他指标均有明显改善。聚左旋消旋乳酸组术后2年的相关指标并没有明显改善,只有6例(50%)的目测类比评分和ODI指数有改善,然而聚醚醚酮组10例(71%)有改善。聚左旋消旋乳酸组中1/3患者在目测类比评分和ODI指数方面有所加重。聚左旋消旋乳酸组3例出现轻度到中度的骨溶解。他们认为尽管影像学上融合率无差异,但对于退变性椎管狭窄患者,聚醚醚酮融合器辅助脊柱融合在减轻术后症状上明显优于聚左旋消旋乳酸融合器。不过,早期对生物可吸收融合器的研究结果表明该技术有较好前景,需要延长随访时间,病例选择得当,见图2。"
| [1] Mcafee PC,Cunningham BW,Lee GA,et al.Revision strategies for salvaging or improving failed cylindrical cages.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1999;24(20):2147-2153. [2] Ohlin A,Karlsson M,Duppe H,et al.Complications after transpedicular stabilization of the spine. A survivorship analysis of 163 cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1994;19(24): 2774-2779. [3] van Dijk M,Smit TH,Sugihara S,et al.The effect of cage stiffness on the rate of lumbar interbody fusion - An in vivo model using poly(L-lactic acid) and titanium cages. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2002;27(7):682-688. [4] 杨进顺,吕浩然,赵玉,等.不同类型椎间融合器的材料学特征及其临床应用效果[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(9): 1755-1757. [5] Johnsson R,Axelsson P,Stromqvist B.Posterolateral lumbar fusion using facet joint fixation with biodegradable rods: a pilot study. Eur Spine J.1997;6(2):144-148. [6] Deguchi M,Cheng BC,Sato K,et al.Biomechanical evaluation of translaminar facet joint fixation. A comparative study of poly-L-lactide pins, screws, and pedicle fixation.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1998;23(12):1307-1313. [7] Vaccaro AR.Bioabsorbable screws.J Neurosurg Spine.2011; 15(4):359-360. [8] Daniels AU,Chang MK,Andriano KP. Mechanical properties of biodegradable polymers and composites proposed for internal fixation of bone.J Appl Biomater.1990;1(1):57-78. [9] Lohfeld S,Cahill S,Barron V,et al.Fabrication, mechanical and in vivo performance of polycaprolactone/tricalcium phosphate composite scaffolds. Acta Biomater.2012;8(9):3446-3456. [10] Chunguang Z,Yueming S,Chongqi T,et al.Evaluation of bioabsorbable multiamino acid copolymer/alpha-tri-calcium phosphate interbody fusion cages in a goat model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2011;36(25):E1615-E1622. [11] 周春光,宋跃明,屠重棋,等. 多元氨基酸共聚物/磷酸钙复合材料椎间融合器的设计制备及压缩强度测试[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2011,28(4):1136-1140. [12] Wuisman PI,Smit TH.Bioresorbable polymers: heading for a new generation of spinal cages.Eur Spine J.2006;15(2): 133-148. [13] Bowlin GL.Encyclopedia of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering. 2nd ed. ed. 2008:1254-1264. [14] Hutmacher DW,Schantz T,Zein I,et al.Mechanical properties and cell cultural response of polycaprolactone scaffolds designed and fabricated via fused deposition modeling.J Biomed Mater Res.2001;55(2):203-216. [15] Gautier SE,Oudega M,Fragoso M,et al. Poly(alpha-hydroxyacids) for application in the spinal cord: resorbability and biocompatibility with adult rat Schwann cells and spinal cord.J Biomed Mater Res.1998;42(4):642-654. [16] Claes L,Ignatius A.Development of new, biodegradable implants. Chirurg. 2002;73(10):990-996. [17] Gautier SE,Oudega M,Fragoso M,et al. Poly(alpha-hydroxyacids) for application in the spinal cord: resorbability and biocompatibility with adult rat Schwann cells and spinal cord.J Biomed Mater Res.1998;42(4):642-654. [18] Smit TH.The use of a quadruped as an in vivo model for the study of the spine - biomechanical considerations.Eur Spine J.2002;11(2):137-144. [19] Smit TH,Muller R,van Dijk M,et al.Changes in bone architecture during spinal fusion: three years follow-up and the role of cage stiffness. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003; 28(16):1802-1809. [20] Debusscher F,Aunoble S,Alsawad Y,et al.Anterior cervical fusion with a bio-resorbable composite cage (beta TCP-PLLA): clinical and radiological results from a prospective study on 20 patients.Eur Spine J.2009;18(9): 1314-1320. [21] Lippman CR,Hajjar M,Abshire B,et al.Cervical spine fusion with bioabsorbable cages.Neurosurg Focus.2004;16(3):E4. [22] Kandziora F,Pflugmacher R,Scholz M,et al.Bioabsorbable interbody cages in a sheep cervical spine fusion model.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2004;29(17):1845-1856. [23] Lazennec JY,Madi A,Rousseau MA,et al. Evaluation of the 96/4 PLDLLA polymer resorbable lumbar interbody cage in a long term animal model. Eur Spine J.2006;15(10): 1545-1553. [24] Lyons AS,Sherman BP,Puttlitz CM,et al.Failure of resorbable plates and screws in an ovine model of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Spine J.2011;11(9):876-883. [25] Coe JD,Vaccaro AR.Instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with bioresorbable polymer implants and iliac crest autograft.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(17 Suppl): S76-S83. [26] Abbah SA,Lam CX,Hutmacher DW,et al.Biological performance of a polycaprolactone-based scaffold used as fusion cage device in a large animal model of spinal reconstructive surgery.Biomaterials.2009;30(28):5086-5093. [27] Ergun A,Chung R,Ward D,et al.Unitary bioresorbable cage/core bone graft substitutes for spinal arthrodesis coextruded from polycaprolactone biocomposites. Ann Biomed Eng.2012;40(5):1073-1087. [28] Lowe TG,Coe JD.Bioresorbable polymer implants in the unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion procedure. Orthopedics.2002;25(10 Suppl):s1179-s1183, s1183. [29] Couture DE,Branch CJ. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with bioabsorbable spacers and local autograft in a series of 27 patients. Neurosurg Focus.2004;16(3):E8. [30] Kuklo TR,Rosner MK,Polly DJ.Computerized tomography evaluation of a resorbable implant after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurg Focus.2004;16(3):E10. [31] Coe JD.Instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with bioabsorbable polymer implants and iliac crest autograft.Neurosurg Focus.2004;16(3):E11. [32] Lanman TH,Hopkins TJ. Early findings in a pilot study of anterior cervical interbody fusion in which recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 was used with poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) bioabsorbable implants. Neurosurg Focus.2004;16(3):E6. [33] Frost A,Bagouri E,Brown M,et al.Osteolysis following resorbable poly-L-lactide-co-D, L-lactide PLIF cage use: a review of cases. Eur Spine J.2012;21(3):449-454. [34] Jiya TU,Smit T,van Royen BJ,et al.Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using non resorbable poly-ether-ether-ketone versus resorbable poly-L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide fusion devices. Clinical outcome at a minimum of 2-year follow-up.Eur Spine J.2011;20(4):618-622. [35] Thomas KA,Toth JM,Crawford NR,et al.Bioresorbable polylactide interbody implants in an ovine anterior cervical discectomy and fusion model: three-year results. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008;33(7):734-742. [36] Kandziora F,Pflugmacher R,Scholz M,et al.Comparison between sheep and human cervical spines: an anatomic, radiographic, bone mineral density, and biomechanical study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2001;26(9):1028-1037. |
| [1] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [2] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [3] | Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian. Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [4] | Yuan Bo, Wang Zhiwei, Tang Yifan, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun. Construction of polycaprolactone-tricalcium phosphate with different mixture ratios using three-dimensional printing technology and its osteoinductivity in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 821-826. |
| [5] | Wang Yang, Nie Jinshan, Gu Zhun, Zhu Kai. Construction and in vitro evaluation of a biodegradable cationic gene delivery system based on hyperbranched polyamidoamine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 936-944. |
| [6] | Leng Yi, Li Zuhao, Ren Guangkai, Wang Zhonghan, Gao Chaohua, Shi Chenyu, Liu He, Wu Dankai. Application and progress of bioactive scaffolds in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 963-970. |
| [7] | Xiong Ying, Xu Yan, Zhou Jianping, Zhang Xujing, Wang Kedian. Electroactive biomaterials in tissue engineering research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5523-5530. |
| [8] | Wei Wei, Liu Yanfei, Zhang Ling, Xiong Na . Self-assembling peptide hydrogel: hemostatic effect and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 310-316. |
| [9] | Zhang Minbo, Peng Qifeng, Ma Yaping, Kong Weijun, Liao Wenbo. Physical properties and biocompatibility of 3D printed bone microparticle/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2215-2222. |
| [10] | Li Zhi, Tan Chunhua, Cai Xianhua, Wang Huasong, Ding Xiaoming, Zhao Yanhong. Fabrication and biocompatibility assessment of the scaffold with biomimetic interconnected macropore structure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2223-2227. |
| [11] | Luo Kai, Yang Yafeng, Ma Teng, Xia Bing, Huang Liangliang, Huang Jinghui, Luo Zhuojing. Effects of perfluorotributylamine/alginate/bioglass biomaterials on viability and osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 1995-2001. |
| [12] | Wang Yuanyuan, Song Wenshan, Yu Dejun, Dai Yuankun, Li Bafang. Preparation and evaluation of fish skin acellular dermal matrix for oral guided tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(10): 1526-1532. |
| [13] | Liu Shaoyang, Zou Hanlin . Biocompatibility of anodic titanium oxide: an experimental research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(10): 1575-1580. |
| [14] | Cai Yuhui, Hu Kesu, Zhang Yi. Biosafety evaluation of chitosan lactate/hyaluronate sponge [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(10): 1558-1563. |
| [15] | Zhang Lei, Zhou Song, Cheng Bao-chang. Actuality and challenge of biomaterials in annulus fibrosus repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(6): 958-963. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||